Turbo-BrainVoyager v4.4
Menu Functions
The following menu functions can be used to quickly access important features of Turbo-BrainVoyager. Additional context menus are available by clicking the right mouse button (or CTRL-Left-Mouse on Macs). Context menus are only accessible when not in real-time analysis mode. In the upper right corner of the program window, there are also two standard buttons for minimizing and exiting the program. Between these two icons is a "Restore" icon, which can be used to toggle between two sizes of the program window. This icon is relevant only for the Windows version of the program since the Mac OS X and Linux versions allow to freely resize the program window. The main control buttons in the left upper region control fundamental operations, i.e. to start the analysis of a real-time scan.
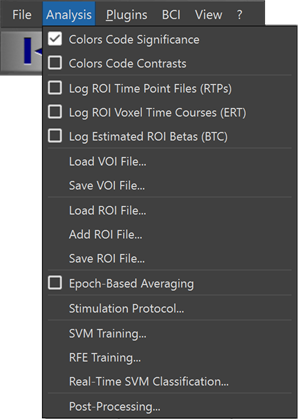
Main menu
- File
- Set New TBV File. Changes current TBV file. Presents a File Open dialog, which you can use to navigate to a new TBV settings file.
- Edit TBV File. This option invokes the TBV Settings dialog.
- Edit MasterTBV File. This menu item invokes the MasterTBV File dialog.
- Rename DICOM Files. This option calls the Rename DICOM Files dialog.
- VMR-VMR Coregistration. This option invokes the VMR-VMR Coregistration dialog allowing to align an intra-session 3D data set with an extra-session (e.g. AC-PC) transformed 3D data set, which is useful for preparing advanced visualizations.
- Close. Removes the current analysis clearing all windows.
- Exit. Quits the program.
- Analysis
- Colors Code Significance. A flag on the left side of this menu item shows whether this mode is currently enabled. In this case, a standard red-to-yellow color scale is used to visualize the significance of a voxel for selected ">" contrasts and a standard blue-to-green color scale is used to visualize the significance of a voxel for "<" contrasts. Note that in this mode, it is not visualized which contrast (or contrasts) are significant at a voxel in case that more than one contrast is selected in the contrast window. You may turn on/off this visualization mode also with the P toggle button.
- Colors Code Contrasts. A flag on the left side of this menu item shows whether this mode is currently enabled. In this case, each significant voxel is visualized with the color of the contrast with the highest t-value. This allows to quickly recognize, which contrast is the most significant at a particular voxel. You may turn on/off this visualization mode also with the P toggle button.
- Log ROI Time Point Files (RTPs). If this option is turned on, a .RTP file is saved for each time point to disk containing the mean signal values of all currently selected ROIs. This can be used for custom software aiming at further analyzing ROI data in real-time. The time point at which a .RTP file was written can be identified by the time point value that is included in the file name. The first value within a .RTP file specifies the number of ROIs at that moment during real-time processing. This is followed by a series of values corresponding to the number of available ROIs. Finally an integer value is stored representing the condition of the current protocol defined at that time point. (Note that the extension is the same as used for real-time protocols, but ROI RTP and protocol RTP files are unrelated).
- Log ROI Voxel Time Courses (ERT). If this option is turned on, the values of all voxels within all currently selected ROIs are saved incrementally to disk in a single .ERT file. This can be used for custom software aiming at further analyzing ROI data at the voxel level in real-time.
- Log Estimated ROI Betas (BTC). This option stores estimated beta values (percent signal change transformed) from GLMs performed on the mean time courses of all currently selected ROIs. The data is incrementally saved into a single .BTC file.
- Load VOI File. This function allows to load VOI files previously saved from TBV or .VOI files prepared with BrainVoyager. These files are defined typically in stereotactic 3D (ACPC or Talairach) space. To work properly, appropriate alignment files must be provided.
- Save VOI File... This function saves all current ROIs as 3D volumes-of-interest (VOIs) to disk in a .VOI file. This option is only enabled if full 3D data sets (intra-session, ACPC or Talairach space) are available. The saved VOI files can be used for further analyses in BrainVoyager and they can be reloaded for subsequent runs.
- Load ROI File. This function (re)loads definitions of regions-of-interest (ROIs) previously saved to disk as .ROI files. A .ROI file contains for each ROI a list of voxel coordinates. Since ROI definition are in functional scan space and not in stereotactic space, they should be only used loaded for runs of the same session and with the same slice position information. Note that you can also use the Pre-Load ROI butto to pre-load defined ROIs from a previous run, e.g. before starting a neurofeedback run.
- Add ROI File. This function adds definitions of regions-of-interest (ROIs) previously saved to disk to the currently defined ROIs.
- Save ROI File. This function saves all current regions-of-interest (ROIs) to disk in a .ROI file. For each ROI, the coordinates of individual voxels are stored in functional scan space (x and y coordinate within a slice and the slice number as the z coordinate). At the end of a real-time run, this function is called automatically to save the state of selected ROIs in a file called "<ProjectName>.roi".
- Epoch-Based Averaging. This option determines how the baseline is computed for the event-related averaging (AVG) plot shown in the 3D view for the currently active ROI. If turned on, percent signal changes are calculated for individual events/blocks with respect to the preceding (baseline) signal level and the calculated percent signal changes are then averaged across repetitions. If this option is turned off (default), a baseline signal level is first computed as the average of the time segments before each event/block and percent signal changes for individual events/blocks are calculated with respect to this common baseline. The results of the latter approach are more in line with those obtained from a General Linear Model (GLM) analysis also estimating a generic baseline level from all available baseline condition epochs.
- Stimulation Protocol. This option invokes the Stimulation Protocol dialog.
- SVM Training. Launches a machine learning tool allowing to train a SVM classifier to associate patterns of activity with different classes (conditions).
- Real-Time SVM Classification. Launches a real-time classification tool that uses a trained classifier to incrementally predict the class to which a current activity pattern belongs.
- Post Processing. Launches tools to perform additional processing steps after a real-time run has been completed to improve the quality of the data beyond the pre-processing routines applied during real-time processing. The processing steps include slice scan time processing and non-linear high-pass filtering.
- Plugins
- This menu shows a list of all available plugins. Select one of the available entries to start the respective plugin. Note that a plugin needs to be invoked before turning on real-time processing of functional data. As default, at least four plugins should be available after program installation, including the real-time ICA plugin and example plugins (available with source code) demonstrating processing of ROIs, export of volume data, and access to a running SVM classifier.
- BCI
- Neurofeedback. This menu item launches the Neurofeedback dialog that offers various functions for presenting data to the subject during real-time scanning.
- BOLD Decoder. This menu item launches the BOLD Decoder tool that can be used to decode spatio-temporal activity patterns evoked by engaging in different mental tasks.
- View
- Multi-Slice View. The scanned first EPI or inplane images are shown in a multi-slice arrangement with superimposed statistical data. This view may also be selected by clicking the Multi-Slice View Icon button or by pressing the F key.
- Volume View. The EPI or inplane images are shown in three subwindows in 3D mode. The three subwindows show a sagittal, coronal and axial plane of the data; the original slice data is stacked on top of each other and interpolated to a 1mm x1mm x 1mm 3D data. This view may also be selected by clicking the Volume View Icon button or by pressing the V key.
- Anatomical Volume View. Shows dynamic contrast maps superimposed on intra- or extra-session 3D data sets. To use this view, preparations have to be performed prior to the functional measurements. This view may also be selected by clicking the Anatomical Volume View Icon button or by pressing the A key.
- Surface View. Shows surface rendered representations of the brain. To use this view, preparations have to be performed prior to the functional measurements. This view may also be selected by clicking the Surface View Icon button or by pressing the S key
- Overlay On First Func Volume. The (statistical) maps are superimposed on the first functional volume of the EPI data of the current run. A flag on the left side of this menu entry indicates whether this display mode is currently selected. The same function is also provided with the I and C toggle keys.
- Overlay On Current Func Volume. The (statistical) maps are superimposed on the currently processed functional (EPI) volume. A flag on the left side of this menu entry as well as the Log pane indicate whether this display mode is currently selected. The same function is also provided with the C toggle key.
- Overlay On Inplanes. If coplanar inplane slices are available, the statistical maps are superimposed on these inplanes. A flag on the left side of this menu entry indicates whether this display mode is currently selected. If no inplanes are available, this option is disabled. The inplanes are often T1-weighted images not suffering from the EPI susceptibility artifacts. The same function is also provided with the I toggle key.
- Show ROIs With Rectangles. This option affects only multi-slice view; it turns on visualization of ROIs as rectangles. This has the advantage that the voxels within the region remain visible (are not marked as when using the Using ROIs As Marked Voxels option) but it has the disadvantage that it is not shown which voxels precisely are included in a ROI. Switching between the different ROI visualizations can be also achieved by pressing CTRL-R.
- Using ROIs With Highlighted Voxels. This option affects only multi-slice view; it turns on visualization of ROIs by marking each voxel belonging to the ROI with a single color. This has the advantage that the voxels making up an ROI are precisely visible but it has the disadvantage that the voxels (e.g. current map values) are not visible well; zooming in a slice (single-slice view) is a good compromise since the enlarged view shows voxels usually large enough to visualize both the rectangle around a voxel labeling it as belonging to a ROI as well as the color inside the rectangle reflecting the voxel's map value or anatomical intensity value. Switching between the different ROI visualizations can be also achieved by pressing CTRL-R.
- Show ROIs With Rectangles And Highlighted Voxels. This option affects only multi-slice view. This option combines the visualization of ROIs with rectangles and with highlighted voxels (see above). Switching between the different ROI visualizations can be also achieved by pressing CTRL-R.
- Show Time Course Container. Invokes the Time Course Container dialog showing time courses and estimated beta weights for all currently selected ROIs. This dialog is also automatically shown when more ROIs are selected than panes available in the main screen.
- Remove ROI Time Course Plots. Removes all open time course plots both those embedded in the main screen (on right side) and those shown in the Time Course Container dialog.
- Display Detrended ROI Time Courses. Shows detrended time courses of ROIs in Time Course Windows in the main window and in the Time Courses Container. The menu item indicates whether detrending is on or off. The function is only available if a linear trend is added as a confound predictor to the design matrix. The D key can also be used to toggle between detrended and raw ROI time courses.
- ? (Help)
- User's Guide. Invokes a documentation viewer showing the Turbo-BrainVoyager User's Guide.
- License Information. Shows information about the license.
- About Turbo-BrainVoyager. Invokes the Turbo-BrainVoyager splash screen with version information (on Mac OS X this item is located in the Turbo-BrainVoyager menu on the left side of the menu bar).
Context Menus
- User's Guide. Invoke the User's Guide providing help about all major features of the software.
- Save as Bitmap.... Saves the program window or the sub-window under the mouse to disk. Presents a "Save As" dialog. Note that this command is context-dependent: If you invoke the context menu over the contrasts overlay window or any of the time course windows, only the content of the respective window is saved. If you invoke it at any other part of the program window, the whole content of the program window is saved.
Copyright © 2002 - 2024 Rainer Goebel. All rights reserved.